Relational Database Concepts
Relational databases store data in tables consisting of rows and columns. Structured Query Language (SQL) is used to interact with relational databases.
1. Creating a Database
- To create a new database, use the following syntax:
CREATE DATABASE database_name;
USE database_name;
- Example: Create and use a database named "school_management".
CREATE DATABASE school_management;
USE school_management;
2. Creating a Table
- To create a table within a database, define columns and data types:
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column1 data_type constraints,
column2 data_type constraints
);
- Example: Create a table named "students".
CREATE TABLE students (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
age INT,
class VARCHAR(10),
admission_date DATE
);
3. Inserting Data
- To add records to a table:
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2)
VALUES (value1, value2);
- Example: Insert data into the "students" table.
INSERT INTO students (name, age, class, admission_date)
VALUES ('John Doe', 14, '8th', '2024-06-01');
- Insert Multiple Rows:
INSERT INTO students (name, age, class, admission_date)
VALUES
('Jane Smith', 15, '9th', '2024-06-02'),
('Sam Brown', 14, '8th', '2024-06-03');
4. Selecting Data
- To retrieve data from a table:
SELECT column1, column2 FROM table_name;
- Examples:
-- Select all records:
SELECT * FROM students;
-- Select specific columns:
SELECT name, age FROM students;
-- With a condition:
SELECT * FROM students WHERE age > 14;
-- Sorting results:
SELECT * FROM students ORDER BY age DESC;
5. Updating Data
- To modify existing records in a table:
UPDATE table_name
SET column1 = value1
WHERE condition;
- Example: Update the class of a student with ID 1.
UPDATE students
SET class = '9th'
WHERE id = 1;
6. Deleting Data
- To remove records from a table:
DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition;
- Example: Delete a student record with ID 2.
DELETE FROM students
WHERE id = 2;
- Delete All Records (Use with Caution):
DELETE FROM students;
ADO & ADO.NET
ADO (ActiveX Data Objects) and ADO.NET are technologies provided by Microsoft for accessing and managing data from databases and other sources. While ADO is an older technology that works in a connected manner requiring continuous interaction with the database, ADO.NET is the advanced version introduced with the .NET framework, designed to work in a disconnected manner, improving efficiency and performance.
ADO (ActiveX Data Objects)
- ActiveX Data Objects (ADO) is a technology used to interact with databases and other data sources. It provides a unified programming interface, allowing developers to use the same set of objects regardless of the underlying data source.
- In ADO, applications typically require long-lived database connections, which means the connection to the database remains open for an extended period. This also involves locking database resources.
- A single Connection object is used in ADO to establish a connection to the database.
- Data is managed using a RecordSet object, which holds data from a single query or a specific data source.
ADO.NET
- ADO.NET is the advanced successor to ADO, introduced as part of the .NET framework. It provides consistent access to various types of data sources, such as relational databases, XML files, and more.
- Unlike ADO, ADO.NET does not require locking or long-lived connections. It uses a disconnected architecture to improve performance and scalability.
- ADO.NET uses separate objects, such as DataSets and DataAdapters, to represent and manipulate data, enabling faster and more efficient access.
- It seamlessly integrates with XML, allowing data to be represented and stored in XML format.
Differences between ADO and ADO.NET
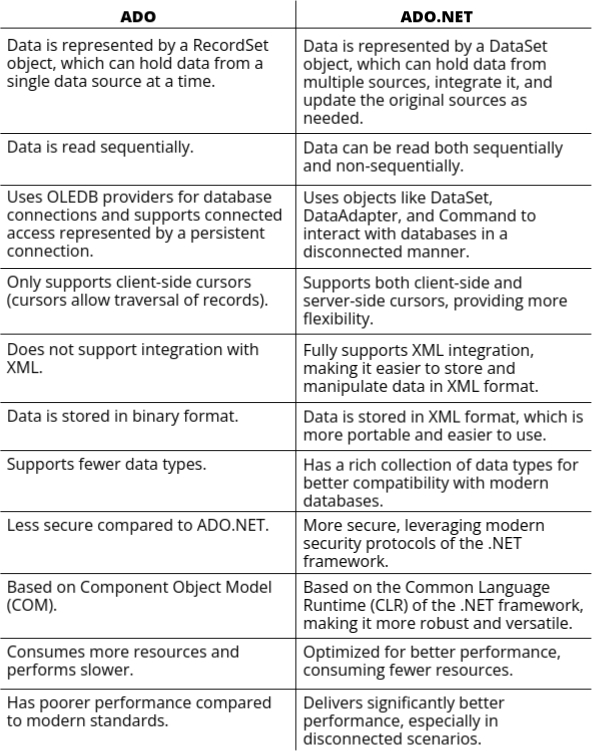
ADO & ADO.NET
Haan, toh baat karte hain ADO aur ADO.NET ke baare mein. Yeh dono hi Microsoft ki technologies hain jo databases aur other data sources ko access aur manage karne ke liye use hoti hain. Bas farak yeh hai ki ADO ek purani technology hai jo connected architecture use karti hai (matlab database se lagatar connection chahiye), jabki ADO.NET ek advanced version hai jo disconnected architecture pe kaam karta hai, aur efficiency aur performance ko improve karta hai.
ADO (ActiveX Data Objects)
- Yeh ek technology hai jo databases aur other data sources ke saath interact karne ke liye use hoti hai. Iska kaam hai ek unified programming interface dena, jisme developer ko har data source ke liye alag-alag cheez seekhni ki zarurat nahi hoti.
- ADO mein applications ko long-lived database connections ki zarurat hoti hai, matlab database connection kaafi der tak open rehta hai. Isse database resources lock hote hain, jo kabhi-kabhi problematic ho sakta hai.
- ADO ek Connection object use karta hai database ke saath connection banane ke liye.
- Data ko manage karne ke liye RecordSet object ka use hota hai, jo ek query ke result ko ya specific data source ke data ko hold karta hai.
ADO.NET
- Ab baat karte hain ADO.NET ki, jo ki ADO ka advanced successor hai aur .NET framework ke sath introduce kiya gaya tha. Yeh alag-alag data sources ko access karne ke liye consistent aur powerful tools provide karta hai.
- ADO.NET mein long-lived connections ki zarurat nahi hoti, aur yeh disconnected architecture use karta hai jo performance aur scalability ko kaafi improve karta hai.
- Data ko represent aur manipulate karne ke liye DataSets aur DataAdapters jaise alag objects ka use hota hai, jo data access ko fast aur efficient banate hain.
- ADO.NET ka ek bada plus point hai iski XML ke saath seamless integration. Data ko XML format mein easily represent aur store kiya ja sakta hai.
Differences between ADO and ADO.NET

Data Providers by .NET Framework
Data Providers .NET Framework mein wo components hote hain jo applications ko data sources jaise SQL Server, Oracle, aur doosre sources se interact karne mein madad karte hain. Yeh providers data source se connection manage karte hain, commands execute karte hain, aur results retrieve karte hain. Har provider ek specific data source ke saath kaam karne ke liye design kiya jata hai.
- .NET Framework Data Provider for SQL Server: Yeh provider Microsoft SQL Server ko access karne ke liye optimized hai. Iske liye System.Data.SqlClient namespace ki zarurat hoti hai aur yeh SQL Server databases ko efficiently aur securely access karta hai.
- .NET Framework Data Provider for OLE DB: Yeh provider un data sources ko connect karne ke liye use hota hai jo OLE DB (Object Linking and Embedding, Database) ka use karte hain. Isme System.Data.OleDb namespace ki zarurat hoti hai aur yeh legacy databases ke liye ideal hai.
- .NET Framework Data Provider for ODBC: ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) ek standard API hai jo database management systems ko access karne ke liye use hoti hai. Yeh provider ODBC drivers use karke data sources ko connect karta hai aur iske liye System.Data.Odbc namespace ki zarurat hoti hai.
- .NET Framework Data Provider for Oracle: Yeh provider specifically Oracle databases ke saath kaam karne ke liye design kiya gaya hai. Isme System.Data.OracleClient namespace ki zarurat hoti hai (jo recent .NET versions mein deprecated hai lekin legacy systems ke liye abhi bhi relevant hai).
.NET Framework Data Provider Objects
.NET Framework data provider kuch core objects provide karta hai jo data operations ko manage karte hain:
- Connection: Yeh object data source ke saath connection establish aur manage karne ke liye use hota hai. Jaise, SQL Server database ke liye SqlConnection object use kiya jata hai.
- Command: Yeh SQL queries ya stored procedures ko execute karne ke liye use hota hai. Example ke liye, SqlCommand SQL Server ke liye aur OleDbCommand OLE DB ke liye use hota hai.
- Data Reader: Yeh forward-only, read-only access provide karta hai data ko jo database se retrieve hota hai. Example ke liye, SqlDataReader SQL Server ke saath use hota hai.
- Data Adapter: Yeh bridge ka kaam karta hai database aur DataSet ke beech. Iska use data ko database se retrieve karne aur uske baad modifications ke baad database mein update karne ke liye hota hai.
.NET mein data provider model kaafi flexible hai aur developers ko alag-alag types ke databases ke saath interact karne ki suvidha deta hai, jisme har database technology ke liye specific namespaces aur classes diye gaye hain. In providers ka use karke developers efficiently data-driven applications likh sakte hain aur different data sources ke saath compatibility maintain kar sakte hain.
Data Providers by .NET Framework
Data Providers in .NET Framework are components that enable applications to interact with data sources such as SQL Server, Oracle, and others. They manage the connection to the data source, execute commands, and retrieve results. Each provider is designed to work with a specific type of data source.
- .NET Framework Data Provider for SQL Server: This provider is optimized for accessing Microsoft SQL Server. It requires the System.Data.SqlClient namespace and provides efficient and secure access to SQL Server databases.
- .NET Framework Data Provider for OLE DB: This provider is used to connect to data sources that use OLE DB (Object Linking and Embedding, Database). It requires the System.Data.OleDb namespace and is ideal for accessing legacy databases.
- .NET Framework Data Provider for ODBC: ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) is a standard API for accessing database management systems. This provider is used to connect to data sources using ODBC drivers and requires the System.Data.Odbc namespace.
- .NET Framework Data Provider for Oracle: This provider is specifically designed to work with Oracle databases. It requires the System.Data.OracleClient namespace (deprecated in recent .NET versions but still relevant for legacy systems).
.NET Framework Data Provider Objects
The .NET Framework data provider includes several core objects that work together to manage data operations:
- Connection: Used to establish and manage a connection to a data source. For example, a connection to a SQL Server database is established using a SqlConnection object.
- Command: Used to execute SQL queries or stored procedures against a database. Examples include SqlCommand for SQL Server and OleDbCommand for OLE DB.
- Data Reader: Provides a forward-only, read-only access to data retrieved from a database. For instance, SqlDataReader is used with SQL Server.
- Data Adapter: Acts as a bridge between a database and a DataSet. It is used to retrieve data from the database and update it back after modifications.
The data provider model in .NET is flexible and allows developers to interact with various types of databases using namespaces and classes tailored for specific database technologies. By using these providers, developers can write data-driven applications efficiently and maintain compatibility with different data sources.