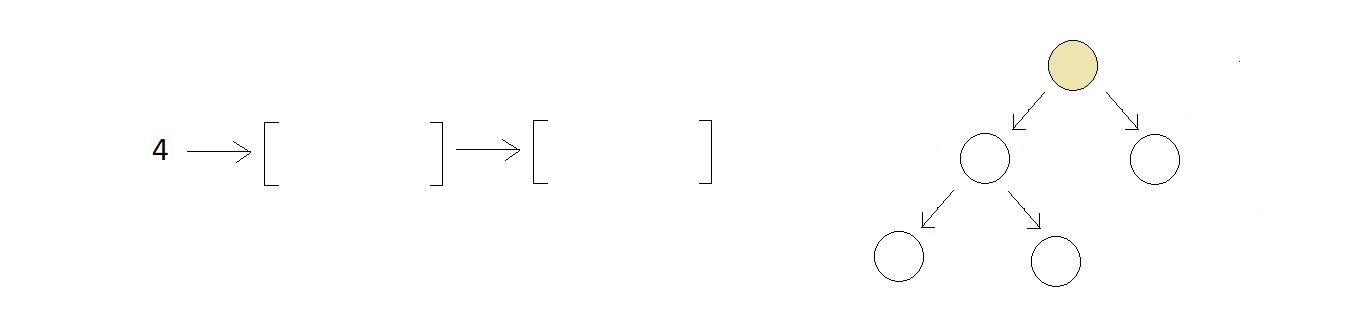PreOrder Traversal Code
We have basic idea that how PreOrder traversal works. Now we'll see that in great detail
- Revision
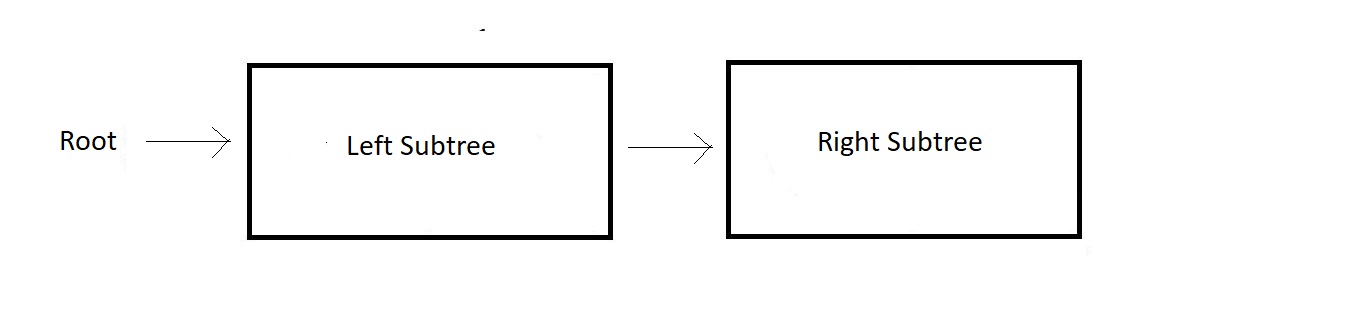
- First start with the root node of the main tree and then get the hold of the left subtree.
- Now consider this left subtree as a new tree, and apply PreOrder on this.
- Recursively doing this with all the further subtrees, you will visit each node of this tree.
- Once left subtree is finished then right subtree is visited and consider this as another tree and repeat the whole thing again.
Example binary tree ↓

- In first step, you visit the root node and mark the presence of left and the right subtree as separate individual trees.
- After you visit the root node, you move to the left subtree considering it as a different tree, and start with its root node.
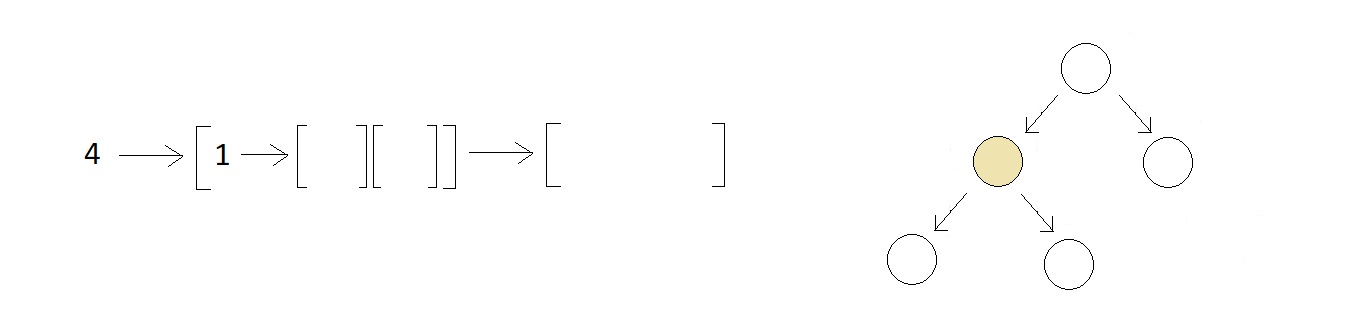
- And then you proceed further with the left and right subtrees of this new tree we considered. And since both the left and right subtrees of this tree have just a single element in them, you finish visiting them, and return back to our original tree.
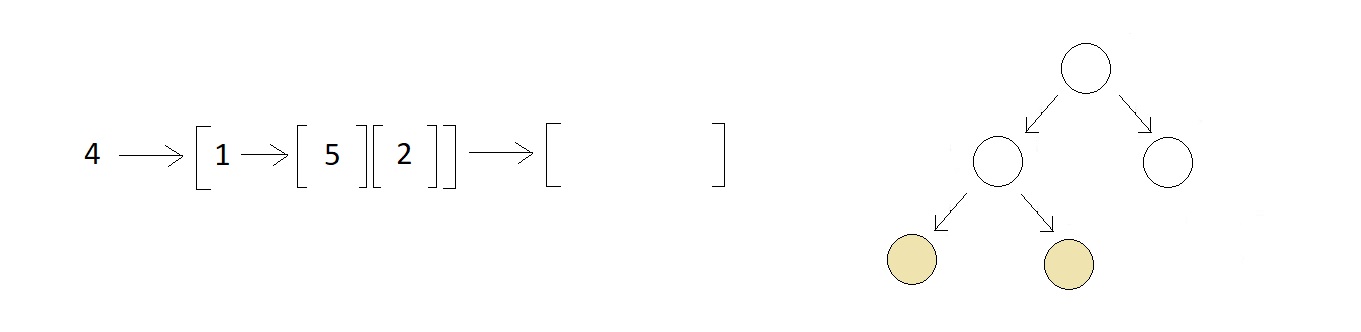
- And finally, we visit the right subtree, and since it contains no left or right subtree further, we finish our preorder traversal here itself.

And our final order of preorder traversal is: 4 → 1 → 5 → 2 → 6.
Now we are ready to implement its programming having studied the flow in detail. I have attached the source code below. Follow it as we proceed.
Code
-
Using createNode function we create nodes and then we link then to each other
// Constructing the root node - Using Function (Recommended)
struct node *p = createNode(4);
struct node *p1 = createNode(1);
struct node *p2 = createNode(6);
struct node *p3 = createNode(5);
struct node *p4 = createNode(2);
// Finally The tree looks like this:
// 4
// / \
// 1 6
// / \
// 5 2
// Linking the root node with left and right children
p->left = p1;
p->right = p2;
p1->left = p3;
p1->right = p4;
- Create a void function preOrder and pass the pointer to the root node of the tree you want to
travers as the only parameter.
- Inside the function, check if the pointer is not NULL, otherwise we wouldn't do anything. So, if it is not NULL, print the data element of the root struct node
- After visiting the root node, simply call the same function recursively on the left and the right
subtrees and you're done.
- Applying recursion does you job in its own subtle ways
- It considers the left subtree as an individual tree and applies preorder on it, and the same goes for the right subtree.
void preOrder(struct node* root){
if(root!=NULL){
printf("%d ", root->data);
preOrder(root->left);
preOrder(root->right);
}
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *left;
struct node *right;
};
struct node *createNode(int data)
{
struct node *n;
n = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
n->data = data;
n->left = NULL;
n->right = NULL;
return n;
}
void preOrder(struct node *root)
{
if (root != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", root->data);
preOrder(root->left);
preOrder(root->right);
}
}
int main()
{
// constructing the root node - Using Function (Recommended)
struct node *p = createNode(4);
struct node *p1 = createNode(1);
struct node *p2 = createNode(6);
struct node *p3 = createNode(5);
struct node *p4 = createNode(2);
// Linkng the rootnode with left and right childre
p->left = p1;
p->right = p2;
p1->left = p3;
p1->right = p4;
preOrder(p);
return 0;
}