What is a union?
- Union is a user defined data type (very similar to structures)
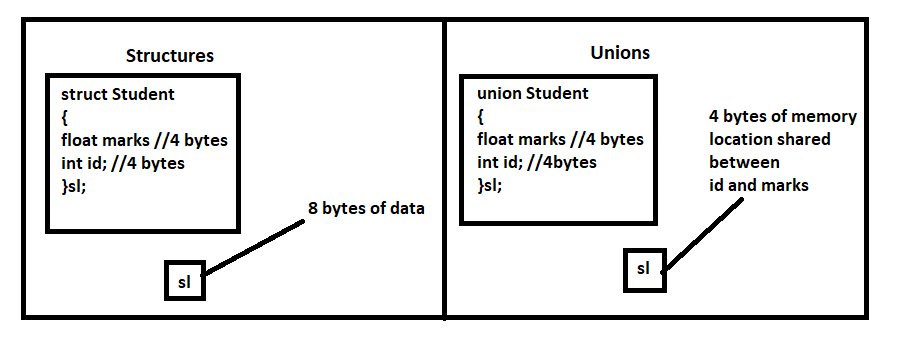
- The difference between structures and unions lies in the fact that in structure, each member has its own strorage location, wereas members of a union uses a single shared memory location.
- The single shared memory location is equal t the size of its largest data member.
Declaring Union
union union_name
{
datatype member1;
datatype member2;
};
//Example Code
union books
{
int pages;
float price;
char title[20];
}b1;
Accessing Union members
We use ". "operator to access the members of a union.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
union Book {
int pages;
float price;
char title[20];
};
int main() {
union Book b1;
b1.pages = 100;
printf( "Pages: %d\n", b1.pages);
b1.price = 250.5;
printf( "Price : %.1f\n", b1.price);
strcpy( b1.title, "C Programming");
printf( "Title : %s\n", b1.title);
return 0;
}
What are similarity between union and structures
- Structure and union are user-defined data types used to store data of different types.
- The members of structure and union can be objects of any type, including other structures and unions or arrays.
- A union or a structure can be passed by value to functions and returned by value by functions.
- '.' operator is used for accessing union and structure members.
What are difference between union and structures
- The keyword union is used to define a union and a keyword struct is used to define the structure.
- Each member within a structure is assigned a unique storage area of location whereas memory allocated is shared by individual members of the union.
- Individual members can be accessed at a time in structure whereas only one member can be accessed at a time in union.
- Altering the value of the member will not affect other
members of the structure, whereas
altering the value of any member will affect other member's values.
Several members of a structure can be initialized at once, whereas only one member can be initialized in union.
Union cannot handle all members at once
why union?
We want our program to take very less memory (no wastage of memory) so it makes our program efficient.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
union Student
{
int id;
int marks;
char fav_char;
char name[34];
};
int main()
{
union Student s1;
strcpy(s1.name, "Harry");
s1.fav_char = 'u';
s1.marks = 45;
s1.id = 1;
//the one which is lastly given value only that variable hold the right value
printf("The id is %d \n", s1.id);
printf("The marks is %d \n", s1.marks);
printf("The fav_char is %c \n", s1.fav_char);
printf("The name is %s \n", s1.name);
return 0;
}
The id is 1
The marks is 1
The fav_char is ☺
The name is ☺